ReDroid (Remote anDroid) is an open source and self-hosting “cloud phone” solution. By running Android in containers on Linux PC, we could access Android desktop by using Scrcpy. And the container could be accessed remotely.
Here is my demonstration of what “self-hosting cloud Android phone” looks like. In this video, I install Scrcpy client on iPhone and connect to Linux PC using Zerotier to play Android games remotely. (sorry my video is in Chinese)
ReDroid is also one of the few solutions to run Android APP on Linux with open source software. Many Android simulators, not to mention cloud phones, are closed source. In contrast, ReDroid is an open source solution except for the ARM translator. Even better, ReDroid supports GPU acceleration plus ARM translations, so you can play more mobile 3D games!
ReDroid is much light-weight and easy to deploy than Android-x86 VM.
If you ask me, there is already a similar, container-based solution, which is known as Waydroid for playing Android games. Why do I choose ReDroid over Waydroid? Well freak Nvidia. Waydroid does not work on Nvidia GPU.
In this article, I will discuss how to use ReDroid to play mobile games on Linux PC. We will setup a ReDroid container, and add ARM translator + Google Service Framework to the ReDroid image for the best experience.
1. Requirements#
Any Linux distribution should be fine.
It is recommended to use a Linux PC with x86 architecture to run Redroid. The ARM architecture support is not very good.
If you have a x86 PC, it can only run x86 architecture Android APPs. However, many mobile games only have ARM architecture versions, so you needs to install the ARM translator (libndk or libhoudini) in the ReDroid container.
To play mobile games, it is recommended that the computer has at least 8GB of RAM, because sometimes ARM takes up a lot of RAM when translating it into x86 instructions.
For GPU acceleration, it is recommended to use Intel or AMD GPUs. 3D acceleration is available out of the box. Nvidia is not recommended.
Regarding the Android version, the redroid:11.0.0-latest and redroid:12.0.0-latest image files released by the Redroid developer have built-in ARM translator libndk developed by Google. I have tried only Android 11 which is relatively stable. GApps It can also be used, so in this article I will uses the Android 11 image .
2. Install dependencies#
ReDroid’s Github has installation instructions for other Linux distributions. I used the Ubuntu.
- First, prepare the binder kernel module. On Ubuntu 24.04 execute the following commands to install the kernel modules:
sudo apt install linux-modules-extra-`uname -r`
sudo modprobe binder_linux devices="binder,hwbinder,vndbinder"
- Make the modules load automatically at boot
sudo cat <<EOT >> /etc/modules-load.d/redroid.conf
binder_linux
options binder_linux devices="binder,hwbinder,vndbinder"
EOT
If you want to integrate the graphical Scrcpy interface with key mapping, you can modify QtScrcpy. You can also try the web version of ws-scrcpy.
3. Pre-install GApps on the RedDroid image#
The image released by the developer of ReDroid is native Android and does not have GApps pre-installed. We can use ayasa520’s Remote-Android Script script to automatically pull the Redroid image and install GApps on it.
This script can also be used to install libndk, libhoudini, Magisk, Widevine DRM and other components.
- Clone the Remote-Android Script repository and create a Python virtual environment
sudo apt install lzip python3 python3-venv python3-pip
git clone https://github.com/ayasa520/redroid-script.git
cd redroid-script
python3 -m venv venv
venv/bin/pip install -r requirements.txt
- Pull the Android 11 image file install GApps
venv/bin/python3 redroid.py -a 11.0.0 -g
- This will build the image
redroid/redroid:11.0.0_gappscontaining GApps.
4. Start the Redroid container with docker-compose#
- This step is only required for Nvidia GPU. Redroid does not support Nvidia GPU well, so it is recommended to use integrated graphics if possible. If you insist on using Nvidia, you have to create a virtual machine to run ReDroid, since Nvidia’s closed-source driver cannot allow ReDroid to use GPU acceleration, you will need to run a QEMU virtual machine and then install ReDroid in it to achieve hardware acceleration through virtio-gpu. However, because virtio-gpu is a para-virtualization, there will be a significant loss in performance. If you do not create a virtual machine and your computer does not have an integrated graphics, ReDroid will use software rendering. If you can accept the performance of software rendering, then there is no need to create a virtual machine.
Create a virtual machine running Redroid.
Download Ubuntu 22.04 ISO, install QEMU + Virt Manager, and create a 64GB Ubuuntu virtual machine
qemu-img create -f qcow2 ubuntu.qcow2 64GB
qemu-system-x86_64 -boot d -cdrom "ubuntu-22.04.1-desktop-amd64.iso" -enable-kvm -smp 4 -device intel-hda -device hda-duplex -device virtio-vga-gl -net nic -net user,hostfwd=tcp::5555-:5555 -cpu host -m 4096 -display sdl,gl=on -hda ubuntu.qcow2
Boot into the virtual machine, and then install Docker.
qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -smp 4 -device intel-hda -device hda-duplex -device virtio-vga-gl -net nic -net user,hostfwd=tcp::5555-:5555 -cpu host -m 4096 -display sdl,gl=on -hda ubuntu.qcow2
- Create a directory to store Android data and create a docker-compose
mkdir ~/redroid
cd redroid
vim docker-compose.yml
- Fill in the following content.
services:
redroid:
image: redroid/redroid:11.0.0_gapps # Use the GApps Redroid image that created before.
stdin_open: true
tty: true
privileged: true
ports:
- 127.0.0.1:5555:5555 # ADB port, to enhance security, set it to only listen to the local localhost port
volumes:
- ./redroid-11-data:/data # The data is stored in the current directory
command:
- androidboot.redroid_width=720 # # Screen resolution
- androidboot.redroid_height=1280
- androidboot.redroid_dpi=320
- androidboot.redroid_fps=60
- androidboot.redroid_gpu_mode=host # host = GPU hardware acceleration, guest = software rendering
- ro.product.cpu.abilist0=x86_64,arm64-v8a,x86,armeabi-v7a,armeabi # Set libndk parameters
- ro.product.cpu.abilist64=x86_64,arm64-v8a
- ro.product.cpu.abilist32=x86,armeabi-v7a,armeabi
- ro.dalvik.vm.isa.arm=x86
- ro.dalvik.vm.isa.arm64=x86_64
- ro.enable.native.bridge.exec=1
- ro.dalvik.vm.native.bridge=libndk_translation.so
- ro.ndk_translation.version=0.2.2
- Start the container
sudo docker compose up -d
- Use ADB to connect to the local ReDroid:
adb connect localhost:5555
# If the connection cannot be made, use the following command to see what is going on inside the container.
sudo docker exec <container ID> logcat
sudo docker logs <container ID>
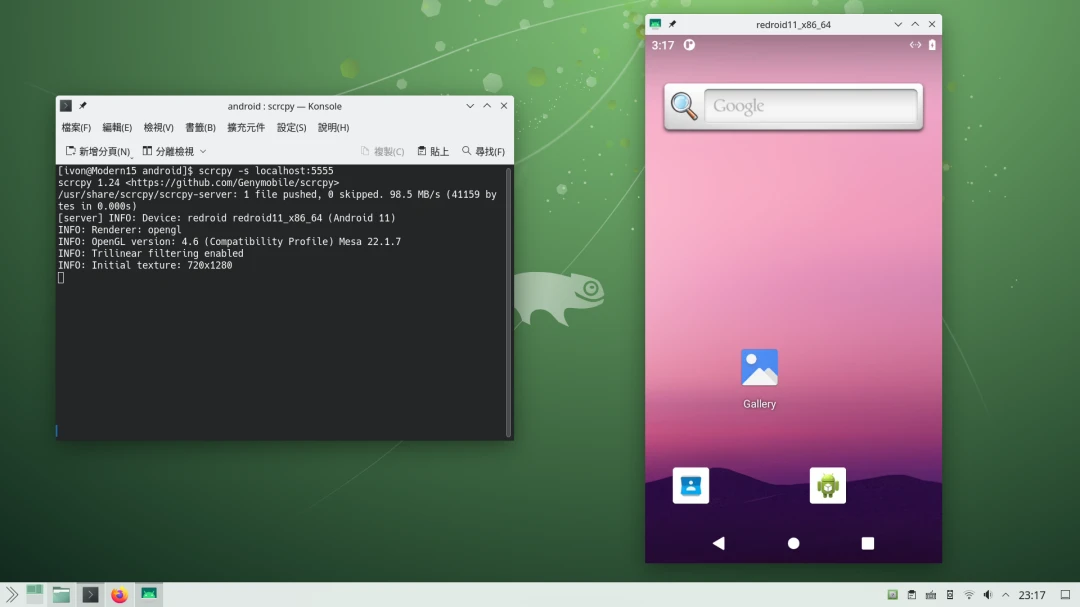
- Execute Scrcpy and connect to Android:
scrcpy -s localhost:5555
You shall see the Android desktop.
Google Play may display “Device not verified”.
Execute the following commands to obtain the Android device ID, go to Google website to register the device, wait 30 minutes and then restart the Redroid container. Then you can log in to Google Play.
adb -s localhost:5555 root
adb -s localhost:5555 shell 'sqlite3 /data/data/com.google.android.gsf/databases/gservices.db \
"select * from main where name = \"android_id\";"'
To confirm whether ReDroid’s 3D acceleration is working properly, please install AIDA64 to see if it can detect the GPU vendor of your PC.
To enhance security, it is recommended to set ReDroid’s docker-compose network to only listen to the localhost’s port (
ports: 127.0.0.1:5000:5000). If you want to open ReDroid to external network access, please be careful to set up the firewall and do not expose ADB’s 5000 port directly to the public network, otherwise there will be serious security concerns.
5. How to install APK on ReDroid#
Currently, even if libndk is installed, the Android 11 Play Store still does not allow downloading of ARM-based APPs. Please use other app stores such as APKPure to install the APP.
In addition to downloading the APK using the browser inside the container, you can also use ADB to install the APK into the Redroid container. For example, download Line’s APK from ApkMirror, and then install it with ADB:
adb -s localhost:5555 install "jp.naver.line.android.apk"
You can also use ADB’s pull and push commands to transfer files.
For screen resolution adjustment, please refer to the instructions of ReDroid and Scrcpy.
6. How to “turn on and off” ReDroid#
If you want to shut down Redroid, close the Scrcpy window and stop the container:
cd ~/redroid
sudo docker compose down
You can use this command to start Redroid later. The /data data of the ReDroid container is located in the ~/redroid/redroid-11-data directory, which can be used to back up files of multiple ReDroid containers.
cd ~/redroid
sudo docker compose up -d
adb connect localhost:5555
scrcpy -s localhost:5555